 kidneys filter your blood by removing waste and excess fluid from your body. This waste is sent to the bladder to be eliminated when you urinate.
kidneys filter your blood by removing waste and excess fluid from your body. This waste is sent to the bladder to be eliminated when you urinate.
Dialysis performs the function of the kidneys if they’ve failed. According to the National Kidney Foundation, end-stage kidney failure occurs when the kidneys are performing at only 10 to 15 percent of their normal function.
Dialysis is a treatment that filters and purifies the blood using a machine. This helps keep your fluids and electrolytes in balance when the kidneys can’t do their job.
Dialysis has been used since the 1940s to treat people with kidney problems.
Properly functioning kidneys prevent extra water, waste, and other impurities from accumulating in your body. They also help control blood pressure and regulate the levels of chemical elements in the blood. These elements may include sodium and potassium. Your kidneys even activate a form of vitamin D that improves the absorption of calcium.
When your kidneys can’t perform these functions due to disease or injury, dialysis can help keep the body running as normally as possible. Without dialysis, salts and other waste products will accumulate in the blood, poison the body, and damage other organs.
However, dialysis isn’t a cure for kidney disease or other problems affecting the kidneys. Different treatments may be needed to address those concerns.
There are three different types of dialysis.
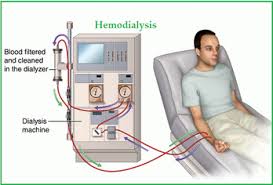
Hemodialysis
Hemodialysis is the most common type of dialysis. This process uses an artificial kidney (hemodialyzer) to remove waste and extra fluid from the blood. The blood is removed from the body and filtered through the artificial kidney. The filtered blood is then returned to the body with the help of a dialysis machine.
To get the blood to flow to the artificial kidney, your doctor will perform surgery to create an entrance point (vascular access) into your blood vessels. The three types of entrance points are:
- Arteriovenous (AV) fistula. This type connects an artery and a vein. It’s the preferred option.
- AV graft. This type is a looped tube.
- Vascular access catheter. This may be inserted into the large vein in your neck.
Both the AV fistula and AV graft are designed for long-term dialysis treatments. People who receive AV fistulas are healed and ready to begin hemodialysis two to three months after their surgery. People who receive AV grafts are ready in two to three weeks. Catheters are designed for short-term or temporary use.
Hemodialysis treatments usually last three to five hours and are performed three times per week. However, hemodialysis treatment can also be completed in shorter, more frequent sessions.
Most hemodialysis treatments are performed at a hospital, doctor’s office, or dialysis center. The length of treatment depends on your body size, the amount of waste in your body, and the current state of your health.
After you’ve been on hemodialysis for an extended period of time, your doctor may feel that you’re ready to give yourself dialysis treatments at home. This option is more common for people who need long-term treatment.
Peritoneal dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis involves surgery to implant a peritoneal dialysis (PD) catheter into your abdomen. The catheter helps filter your blood through the peritoneum, a membrane in your abdomen. During treatment, a special fluid called dialysate flows into the peritoneum. The dialysate absorbs waste. Once the dialysate draws waste out of the bloodstream, it’s drained from your abdomen.
This process takes a few hours and needs to be repeated four to six times per day. However, the exchange of fluids can be performed while you’re sleeping or awake.
There are numerous different types of peritoneal dialysis. The main ones are:
- Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD). In CAPD, your abdomen is filled and drained multiple times each day. This method doesn’t require a machine and must be performed while awake.
- Continuous cycling peritoneal dialysis (CCPD). CCPD uses a machine to cycle the fluid in and out of your abdomen. It’s usually done at night while you sleep.
- Intermittent peritoneal dialysis (IPD). This treatment is usually performed in the hospital, though it may be performed at home. It uses the same machine as CCPD, but the process takes longer.

